Pythagorean Theorem -
The Pythagorean Theorem was most likely introduced in eighth grade math or Algebra 1. If you have already done those, you might remember this, but for those who don't, here it is.
Basically, the Pythagorean Theorem states that for all right triangles, the value of the length of the two shorter sides (the legs) squared (individually; not added then squared) then added together equals the length of the hypotenuse. The equation is:
A and B are the legs, and C is the hypotenuse (for those who don't know, the hypotenuse is the leg that is the longest in a triangle, and in a right triangle, it is the side opposite the right angle). There are many proofs for this, so I won't show many (will put them in later). Example:
Area of Rectangular Prisms and Special Rectangular Prisms (Cubes)-
The area of a cube is fairly simple. It is just the side lengths all multiplied. If you have a 8*8*8 cube, then the volume (the amount of space that an object uses) is equal to 8^3, or 512. For rectangular prisms, the volume is just all the side lengths multiplied. For instance, if you have a 7*5*10 prism, then the area is 7*5*10, or 350. Pretty simple. It also works with prisms that are shaped like a 3D parallelogram. With the parallelograms, you can find the base area and then multiply it by the height.

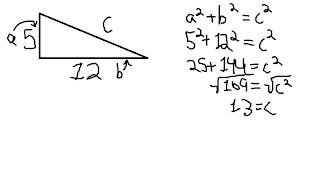
No comments:
Post a Comment